
The negative values imply that the value lies below the mean and positive values tell you that the data point lies above the mean. Now, subtract all the data points from the mean.įigure 5: Difference between heights and mean This means that on average, a dog is 394mm tall. You first find the mean, or the average of all these values by adding them all up and dividing the resulting sum by the number of data points. Now, understand standard deviation with the help of an example.Ĭonsider the example of heights of dogs given below: This leads to more variation in the data, and hence, the curve is more spread out or has a higher standard deviation. Some people might be businessmen, while others might not even have a fixed income. There are also more people doing different jobs which all pay at a very different level. In an urban city, the population is more. Most people here make the same average income, as seen by the high peak at the mean. They all earn more or less the same, with the zamindar earning the most.

In rural areas, say a farming village, most people work in the same profession - farming. Consider the example of income in rural and urban areas.

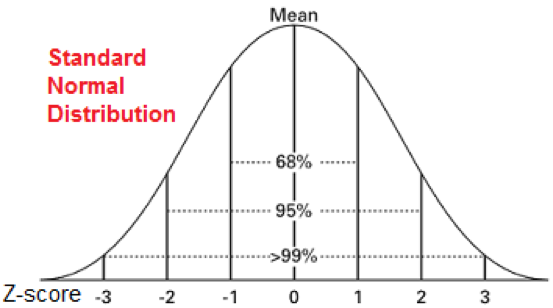
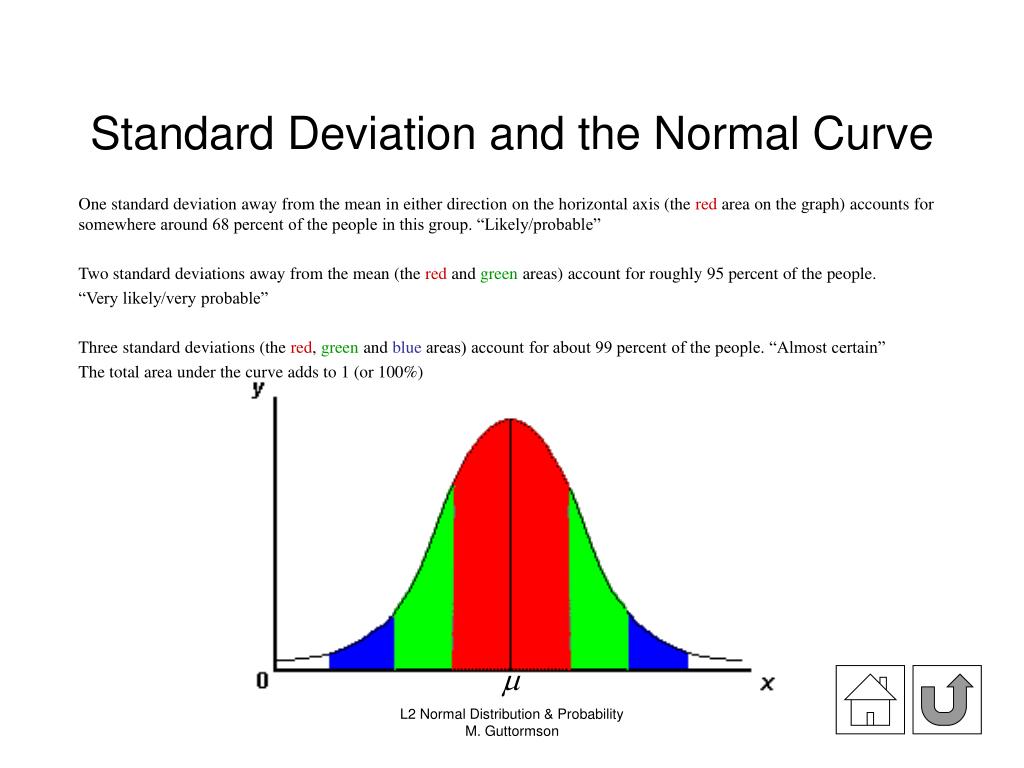
It tells you how narrow or wide the bell curve is. Like how the mean tells you where the data is centered, the standard deviation gives you the width of your bell curve. The square root of the variance gives you the standard deviation. You can calculate it by subtracting each data point from the mean value and then finding the squared mean of the differenced values this is called Variance. The standard deviation measures how far apart the data points in your observations are from each. The standard deviation is a measure of how the values in your data differ from one another or how spread out your data is. This kind of curve is called a Bell Curve, and it is a common feature of a normal distribution. As you move away, the probability density decreases too. Apart from this, most data is around the mean. Consider the below graph which shows the probability distribution of heights in a class:įrom the above graph, you can see that the distribution is mostly about the mean or the average of all heights. The resulting curve is symmetrical about the mean and forms a bell-shaped distribution. The data distribution decreases as you move away from the center. This means that the distribution has more data around the mean.
NORMAL DISTRIBUTION PERCENTAGES PER STANDARD DEVIATION SERIES
The Complete Guide to Skewness and Kurtosis Lesson - 15Ī Holistic Look at Bernoulli Distribution Lesson - 16Īll You Need to Know About Bias in Statistics Lesson - 17Ī Complete Guide to Get a Grasp of Time Series Analysis Lesson - 18 The Definitive Guide to Understand Spearman’s Rank Correlation Lesson - 12Ī Comprehensive Guide to Understand Mean Squared Error Lesson - 13Īll You Need to Know About the Empirical Rule in Statistics Lesson - 14 Understanding the Fundamentals of Arithmetic and Geometric Progression Lesson - 11 The Best Guide to Understand Bayes Theorem Lesson - 6Įverything You Need to Know About the Normal Distribution Lesson - 7Īn In-Depth Explanation of Cumulative Distribution Function Lesson - 8Ī Complete Guide to Chi-Square Test Lesson - 9Ī Complete Guide on Hypothesis Testing in Statistics Lesson - 10
The Ultimate Guide to Understand Conditional Probability Lesson - 4Ī Comprehensive Look at Percentile in Statistics Lesson - 5 The Best Guide to Understand Central Limit Theorem Lesson - 2Īn In-Depth Guide to Measures of Central Tendency : Mean, Median and Mode Lesson - 3
Everything You Need to Know About the Probability Density Function in Statistics Lesson - 1


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
